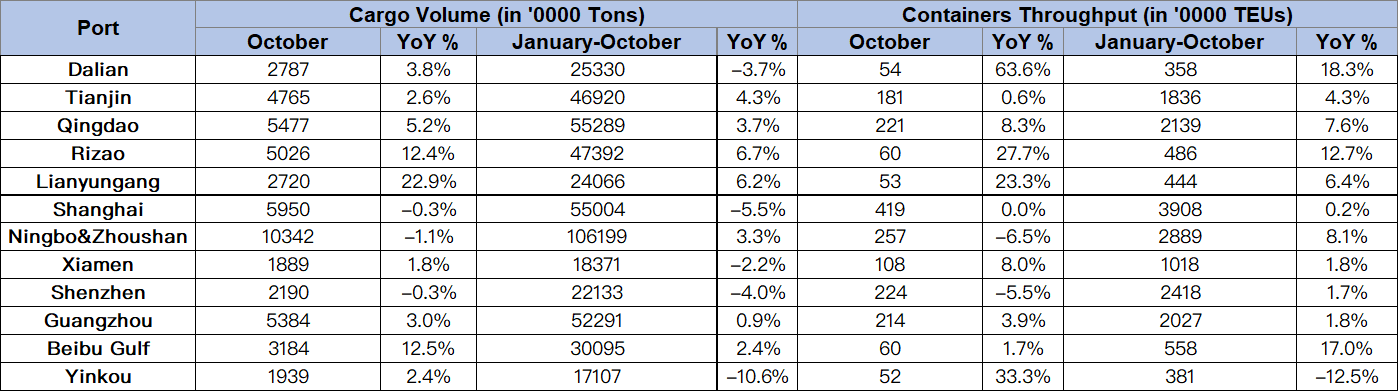
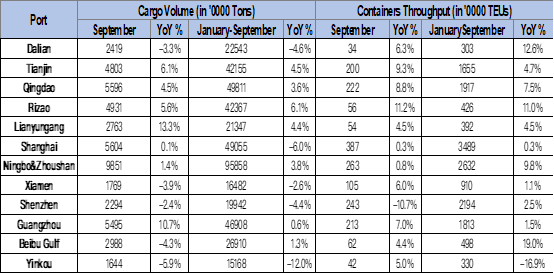
The container throughput of the 12 major Chinese ports was 44.1 million TEUs in the first two months of the year, representing a year-on-year slight increase of 1.3%.
In the same period, the total cargo volume of the ports in China was 2.4 billion tons, translating to a growth of 2.6% compared with the same period last year.
The following chart shows the cargo throughput and container throughput of the 12 major ports in China.
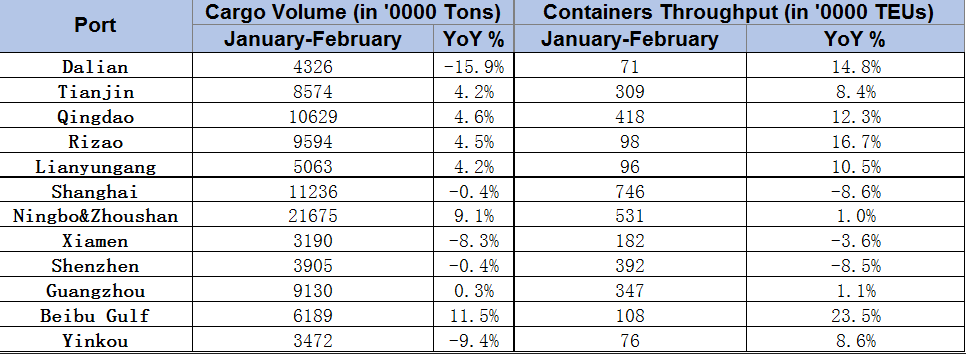
As seen in the table, the port of Shanghai has maintained its dominance, being the busiest container port in the country with 7.46 million TEUs despite the important decline of 8.6% compared with the same months in 2022. The port of Ningbo & Zhoushan is the second busiest box port in China with 5.31 million TEUs, achieving a noteworthy year-on-year growth of 9.1%. In third place, we find the port of Qingdao with 4.18 million TEUs, translating to a year-on-year increase of 12.3%.
Meanwhile, the largest percentage growths were registered at the ports of Dalian, Beibu Gulf and Rizao. Dalian reported year-on-year box growth of 14.8%, Beibu Gulf achieved a 23.5% container increase and Rizao saw its TEUs volumes rise 16.7%.
On the other hand, Shenzen port reported the second biggest year-on-year decline in container volumes, after Shanghai, handling 3.92 million TEUs, translating to an 8.5% drop.
Source: Container News